Phrase-BERT: Improved Phrase Embeddings from BERT with an to Corpus Exploration
Introduction
The phrase BERT paper aims to tackle a challenging task, namely how do we generate quality static embeddings for short phrases. Traditionally BERT style language model embeddings are optimized to embed longer sequence and performance may degrade when applied to shorter phrases.
-
What are some reasons for poor BERT performance when embedding phrases?
1) BERT never sees short phrases during pretraining
2) BERT relies heavily on lexical overlap to determine semantic relatedness
- What are the major contributions of the phraseBERT paper
- contrastive finetuning objective for better phrase representations
- applications to develop neural topic models with better human evaluation scores
-
Example semantic composition of a phrase
“dog house” should be similar to “kennel” in the embedding space
Related Work
- Previous work to phraseBERT sought to define a
composition functionto combine word embeddings into a phrase embedding- most of these related works were pretransformers
Method
-
The phraseBERT paper proposes two distinct
finetuning approaches1) Finetunes on lexically diverse paraphrases
2) Finetunes on phrases in context
- phraseBERT generates a dataset of lexically diverse paraphrases by a
GPT-2 diverse paraphrasing model- decode with nucleus sampling and constraints that non stopwords from original phrase cannot appear
- create negative examples by distorting phrase before feeding into paraphraser
- phraseBERT creates a dataset of phrases in context by taking the 100k most common phrases from the
book3 corpus- part of the PILE
- note: they only store one positive context per phrase
- an extension could be to store multiple
- phraseBERT finetunes using the same
triplet loss objectivefrom sentence BERT- want embeddings for positive sample to be more similar
- want embeddings for negative sample to be more different
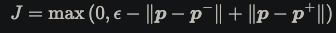
-
The contrastive objective in phraseBERT seeks to push positive samples
together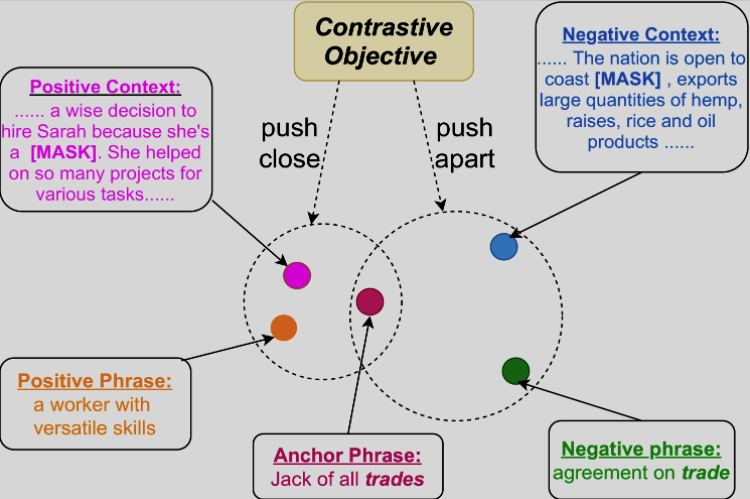
Results
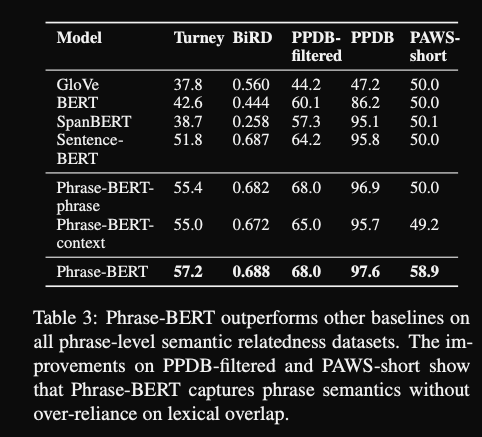
- phraseBERT results: outperforms baselines on
phrase level semantic relatednessdatasets- note: given that it was finetuned on a bunch of phrases how many phrases in these datasets fall in that finetuning set.
- note: Sample PAWS to short examples
- note: finetuning on phrases in context seems to work better
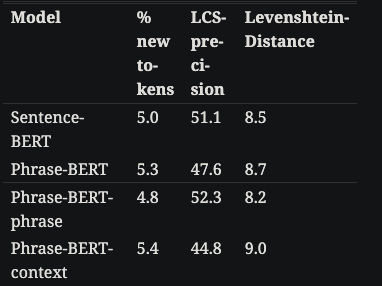
- phraseBERT nearest neighbors of phrase embeddings have
higher lexical diversitythan SBERT- minor difference
- phraseBERT also applied the learned phrase embeddings to topic modeling with good results
- However I don’t find this that interesting
Conclusions
This paper proposes two principled ways to leveraging standard contrastive self supervised pretraining to improve embeddings of short phrases. This is important because short phrases may have different semantic meaning despite high lexical overlap. The method is relatively successful at this goal. The lexical diversity and coherence of nearest neighbor phrases are very impressive. A simple extension would be to sample more than one ground truth context to speed up contrastive learning. I believe much of this model’s performance is dependent on the performance of the GPT2 diverse paraphrase model. I think for training one could come up with a better way to generate paraphrase.
Reference
@article{wang2021phrase,
title={Phrase-bert: Improved phrase embeddings from bert with an application to corpus exploration},
author={Wang, Shufan and Thompson, Laure and Iyyer, Mohit},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.06304},
year={2021}
}
