Ontology-enhanced Prompt-tuning for Few-shot Learning
Introduction
-
What is the name of the OntoPrompt paper?
Ontology-enhanced Prompt-tuning for Few-shot Learning
- What are the main contributions of the OntoPrompt paper?
- ontology tranformation process to convert structured knowledge to text
- span sensitive knowledge injection inject external knowledge but avoid injecting noise
- collective training jointly train representation: inject ontology tokens
-
OntoPrompt works for three tasks:
relation extraction, event extraction and knowledge graph completion - What are some challenges with injecting knowledge for few shot learning?
- missing knowledge: external knowledge base may be missing information
- knowledge noise: knowledge might not be beneficial for downstream tasks
- knowledge heterogeneity: difference in language between downstream tasks and injected knowledge source
-
OntoZSL incorporate ontology prior knowledge for
class semantics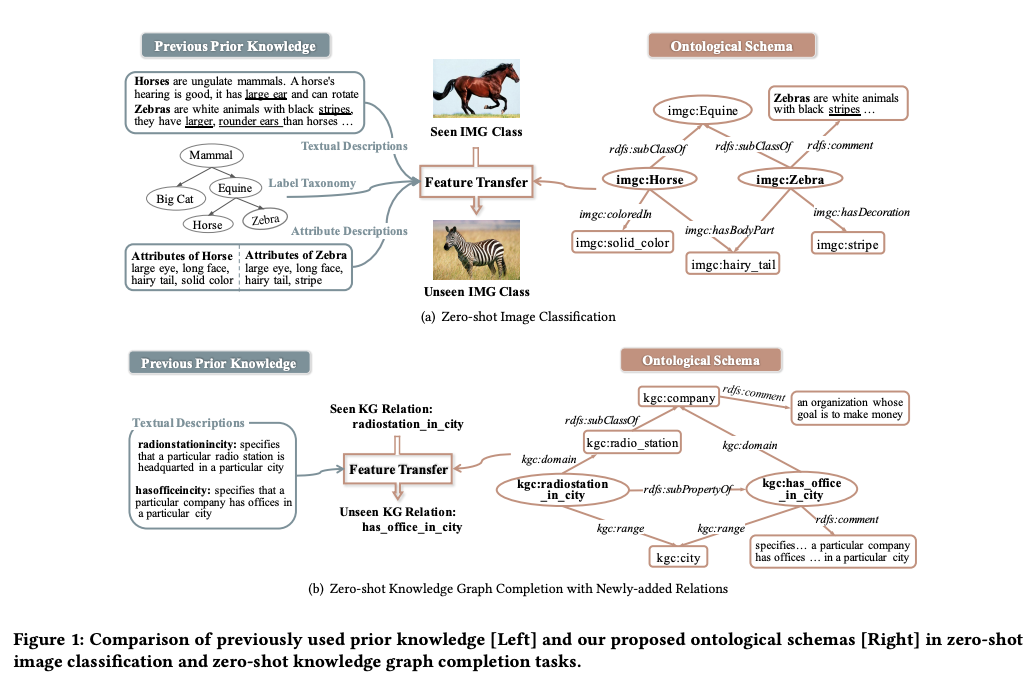
Method
-
In ontoprompt auxiliary knowledge is
converted into textandappend them to input sequence - In OntoPrompt how is the reference ontology formulated?
- $\mathbb{O}= {\mathcal{C}, \mathcal{E}, \mathcal{D}}$
- C is set of concepts
- E are connected edges
- D textual description of each ontology
- OntoPrompt is applied to relation extraction
- named entity descriptions from MUC
- use external textual descriptions in prompt as well as virtual tokens
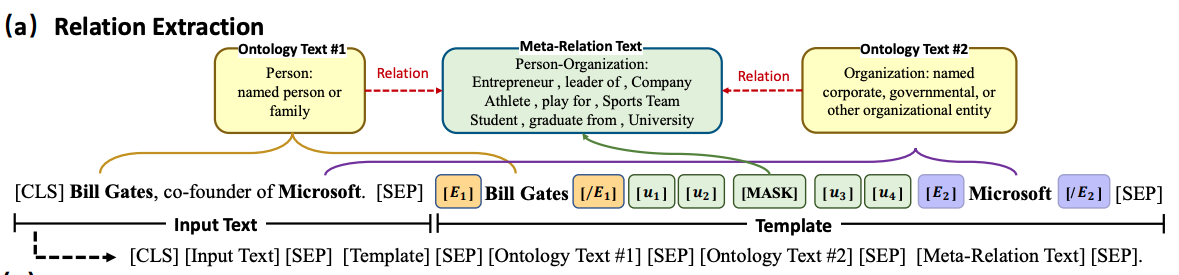
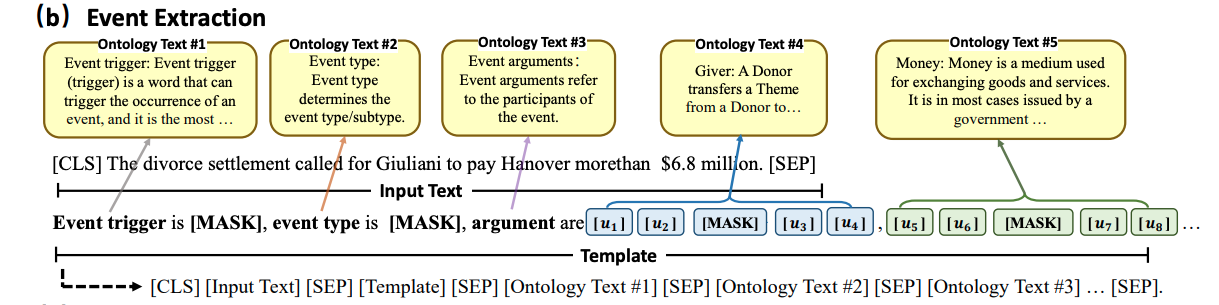
- OntoPrompt for event extraction: prompt has MASK tokens for
Event trigger, event type and each event argument- each one is enhanced with ontology descriptive text
- OntoPrompt for knowledge graph completion is framed as a
triple classification task- get ontology descriptions from wikidata
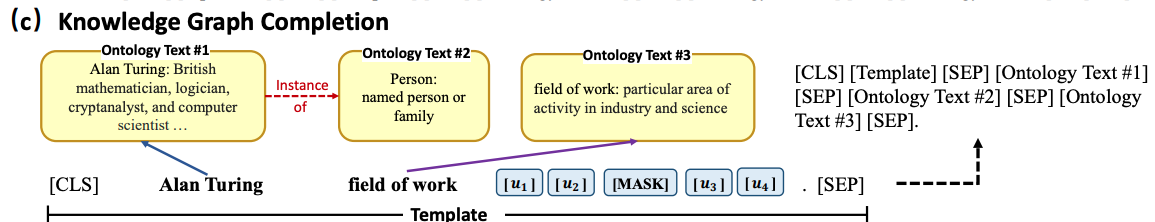
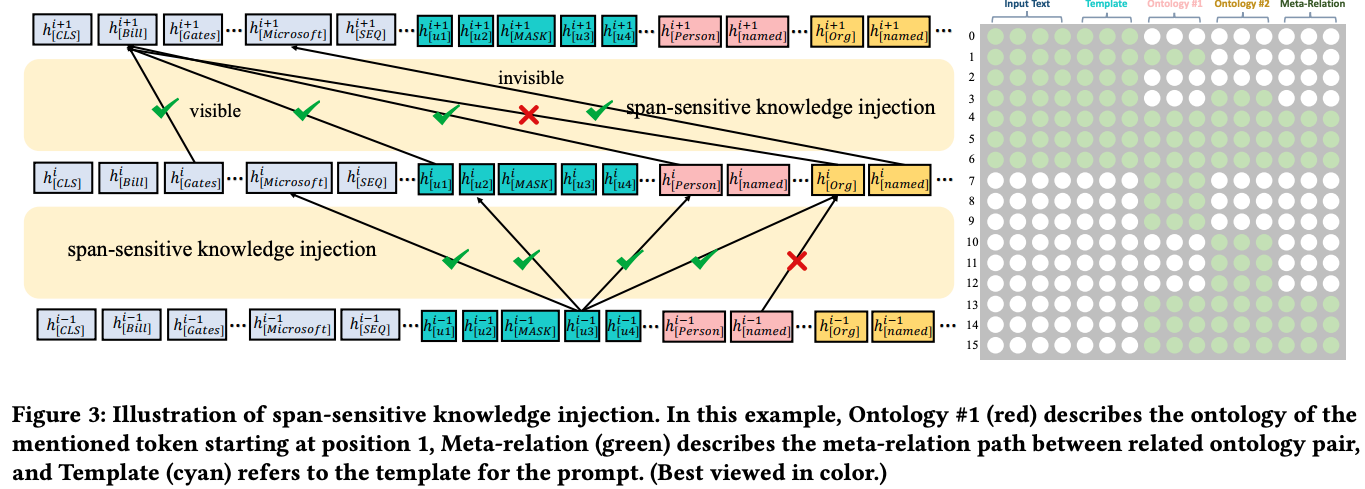
- OntoPrompt span sensitive knowledge injection is done with a
custom attention mask- input can attend to itself
- tokens within each ontology and template can attend to themselves
- span for mentioned entities can attend to their own entity descriptions
- template tokens attend to everything
- OntoPrompt collective training
optimizes ontology tokensthen finetunes entire model- ontology tokens are initialized from
- similar to two stage training in DART (same author)
Results
-
OntoPrompt ablation: span sensitive knowledge injection leads to
small boost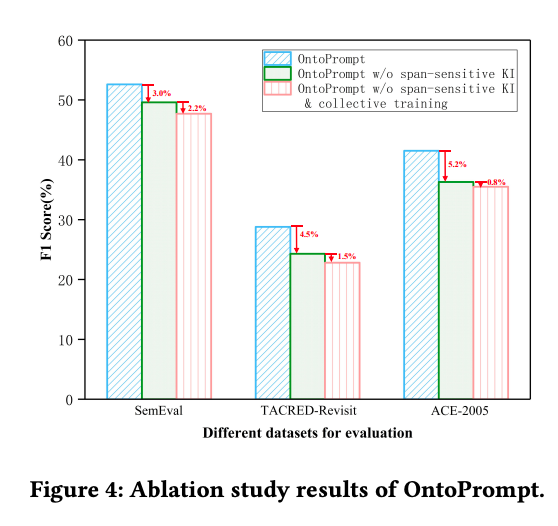
-
OntoPrompt RE results: beats
GDPNET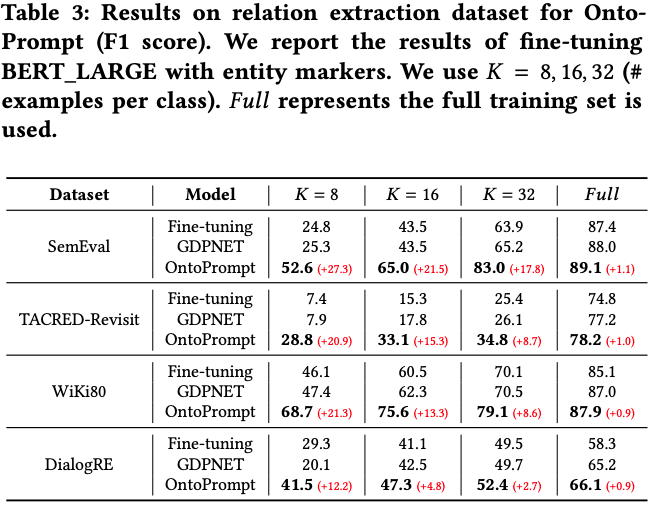
-
OntoPrompt case study: interpretability by looking at
nearest neighbors of virtual tokens
Conclusions
This paper extends the training of virtual tokens in DART to enhance few shot performance on new types of NLP tasks. The injection of text from an external knowledge ontology is very similar to the metadata shaping and TaBi methods.
