Memorizing Transformers
Introduction
-
What is the name of the memorizing transformers paper?
Memorizing Transformers
Yuhuai Wu, Markus N. Rabe, DeLesley Hutchins, Christian Szegedy
- What are some related works to the Memorizing Transformers paper?
- Approximate Linear Attention mechanisms
- Linformer
- Performer
- Pooling Strategies
- hierarchical 1d attention
- Combiner
- Sparse Strategies:
- Bigbird
- Routing Transformer
- Caching Strategies
- TransformerXL
- Compressive transformer
- Retrieval Mechanisms:
- REALM
- RAG
- RETRO
- Approximate Linear Attention mechanisms
- What are the key contributions of the memorizing transformers paper?
- retrieves exact values from memorized context
- don’t compress or average like in compressive transformer
- Do not backpropagate into external memory
- Model complexity improves with size of external memory
- Model’s can generalized to larger memory sizes than they were trained on
- Model is straightforward to incorporate into existing code bases
- retrieves exact values from memorized context
Method
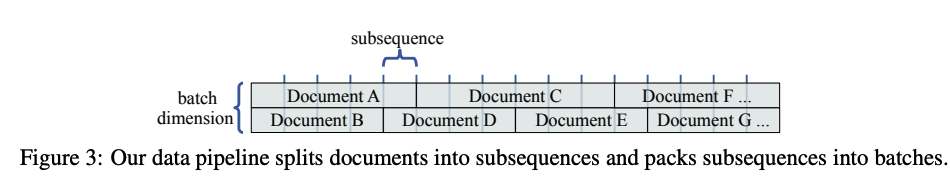
- Similarly to TransformerXL subsequences of documents in the training data are
not shuffledin memorizing transformer- data pipeline keeps documents together:
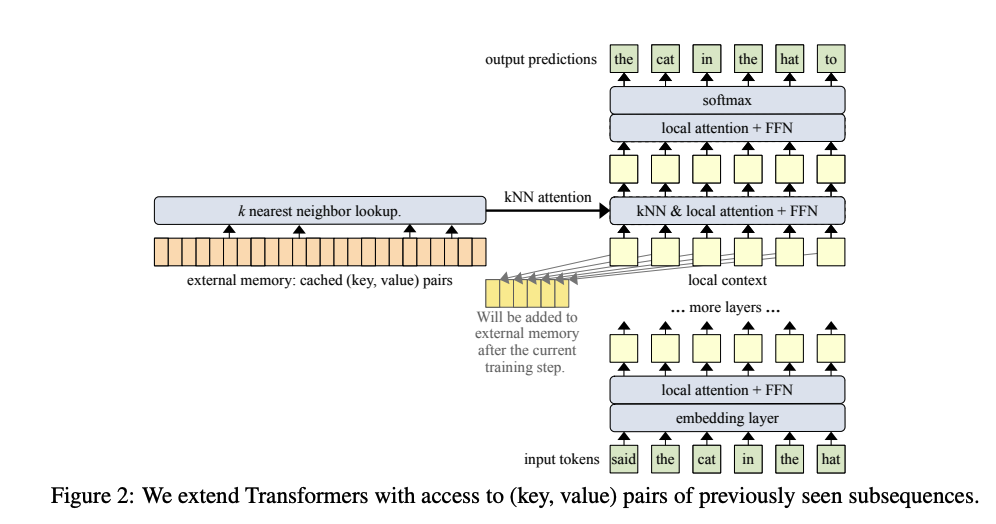
- The memorizing transformer method consists of three major components
- kNN augmented attention layer
- Distributional Shift
- Approximate KNN: use recall of 90% for efficiency
- state that results are robust to this approximation
- Memorizing Transformer kNN augmented attention layer also queries the
keys and values stored in external memory- If the document is very long, old (key, value) pairs will be dropped from the memory to make room for new ones.
- Stores memory for each attention head
- Memorizing transformer results from kNN and local attention are aggregated using a
learned gate- most of the time heads learn to attend to external memory
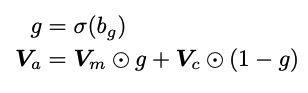
- In order to mitigate staleness of key-value pairs in memory that were encoded by an older model, Memorizing Transformer
normalizesthe keys and queries- still are encoded with an older model
- MOCO solves the same problem in a different way
- At least the distribution will be the same
- In memorizing transformers the memory is
clearedat the start of every new document
Results
- Memorizing Transformer evaluates on documents involving
long form textEnglish language books (PG-19), long web articles (C4), technical math papers (arXiv Math), source code (Github), and formal theorems (Isabelle).- Filter C4 to articles with > 4096 tokens
- Memorizing Transformer perplexity performance is comparable to a vanilla transformer that has
5times the number of parameters- Similar to performance comparison between GOPHER and RETRO
-
Memorizing Transformer perplexity performance scales
positivelywith model size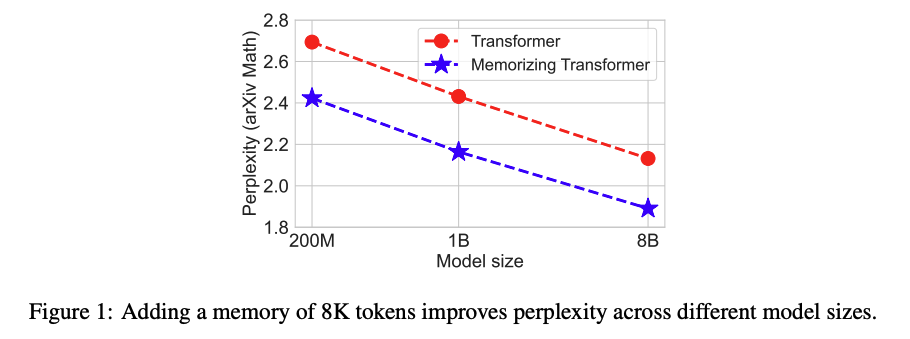
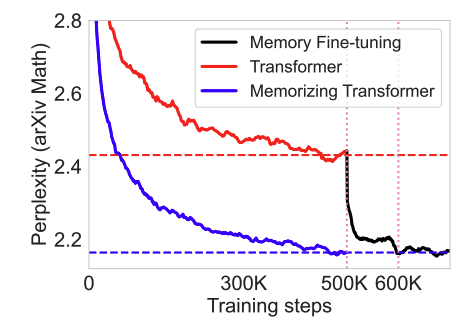
- Finetuning a pretrained model to use Memorizing Transformer external memory is
spectacularly successful- note the instant drop in perplexity
-
Memorizing transformer interpretability: transformer tends to look up
citations, function signatures and theorem definitionsfrom memory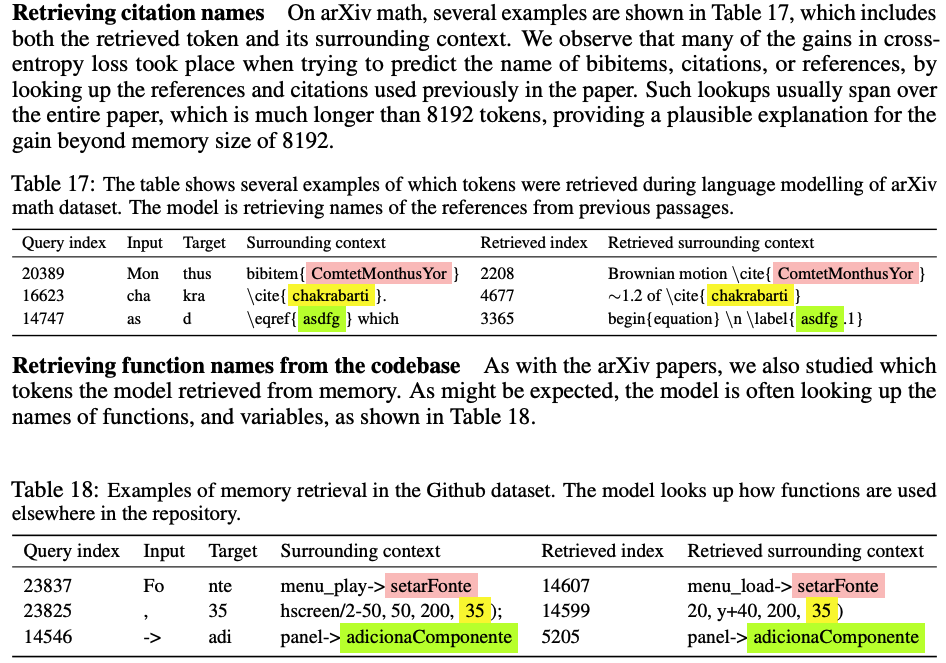
Conclusions
This paper presents a simple approach with empirically good results. While it would be nice to see results on downstream tasks, the gains on the pure language modeling are significant and similar to TransformerXL the method has enough novelty to stand on its own. However, I would have like to see some analysis that could more quantitatively measure gains on long range modeling tasks. The examples of retrieved nearest neighbors provide good qualitative support for an approach but long more long range NLP tasks would be interesting to see. Given that it is possible to adapt PLM to use memorization I believe that this technique could become widely used. It would be interesting to combine memorization with retrieval approaches such as RETRO in order to provide maximum useful context to a language model.
Reference
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2203.08913.pdf
