DiffCSE: Difference-based Contrastive Learning for Sentence Embeddings
Introduction
-
What is the name of the DiffCSE paper?
DiffCSE: Difference-based Contrastive Learning for Sentence
MIT, Meta, Yoon KIm
-
What are the main contributions of the DIFFCSE paper?
- improvement on STS tasks
- embedding method that is aware of edited sentences
Method
- What previous work showed equivariance to be harmful in contrastive learning of text embeddings?
- SIMCSE: using an MLM to replace 15% of words to get positive pairs works less well
- Deletion /Insertion based augmentations work less well
- The idea behind DIFFCSE is to be
sensitive but not invariant tocertain transformations- encoder should be equivariant but not invariant to MLM based augmentations
-
DIFFCSE generated augmented instances by
masking out random tokens and sampling from a LM -
What is the technical definition of equivariance?
$f(T(x)) = T’(f(x)$ where $T’$ is the identity transformation
- we say f is trained to be invariant to T
- Can relax $T’$ to include a broader class of transformations in order to be equivariant
- DiffCSE contains a
conditional discriminatorthat predicts that difference between original and edited sentences- note that there are 3 model components: Encoder, Generator and Discriminator
- ELECTRA style discriminator is conditioned on encoder representation of original sentence
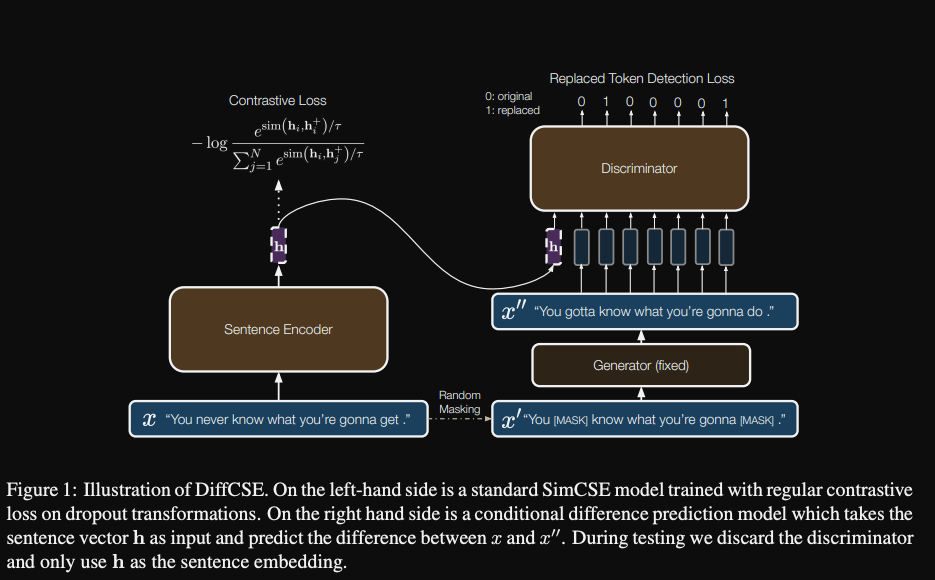
- The DIFFCSE finetuning objective combines standard contrastive loss with
replaced token detection loss- RTD loss is backpropagated through the encoder

- The intuition behind DIFFCSE is that it trains the encoded sentence representation to
distinguish itself from edited transformations
Results
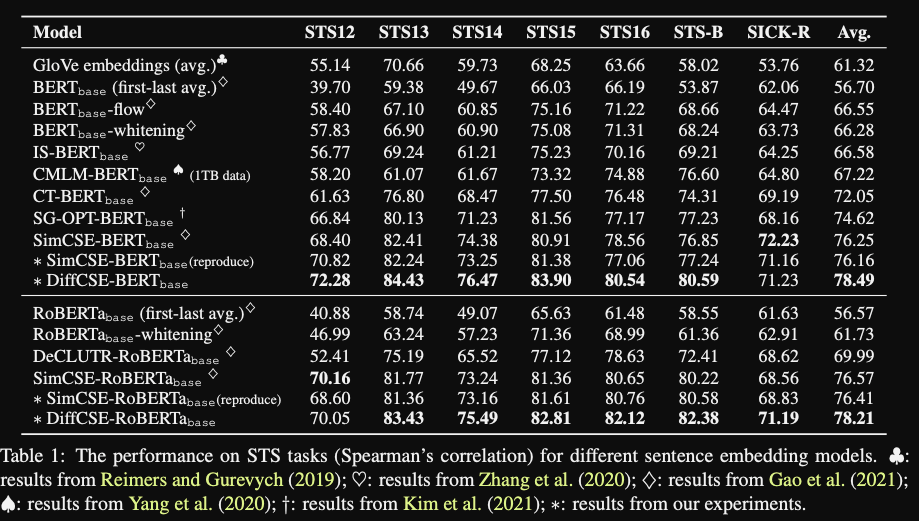
- DIFFCSE results: high scores on
STStasks- note that concurrent work promptBERT gets better results (79.15 STS avg)
-
DiffCSE senteval results: gets
highest average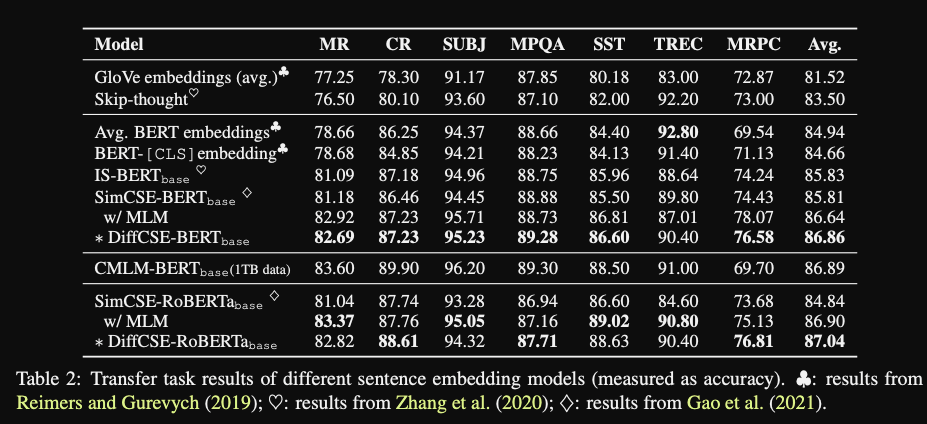
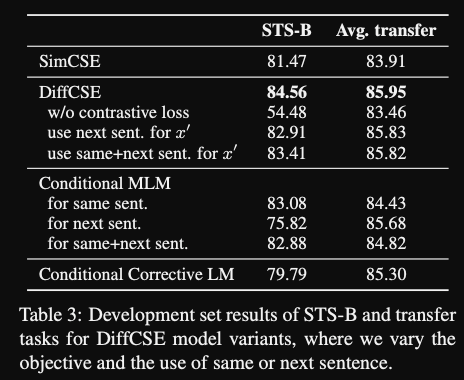
- DIffCSE ablations: using next sentence for RTD loss leads to
worse results- also using CMLM instead of ELECTRA style RTD leads to slightly worse results (but still better than SIMCSE)
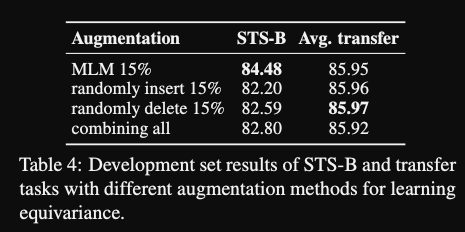
- DIFFCSE augmentation ablations:
MLM performs best- insertion: ELECTRA has to predict which tokens are inserted
- DIFFCSE uses a
two layer pooler with batchnormas a pooling method- two layer MLP
class ProjectionMLP(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden_size): super().__init__() in_dim = hidden_size middle_dim = hidden_size * 2 out_dim = hidden_size self.net = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(in_dim, middle_dim, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm1d(middle_dim), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Linear(middle_dim, out_dim, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm1d(out_dim, affine=False)) -
Sentence embeddings from DIFFCSE appear to have better
alignment but not uniformity
Conclusions
This work proposes an innovative method for unsupervised learning of sentence embeddings that achieves SOTA results. It is slightly behind the STS results reported by the much simpler method promptBERT. However promptBERT does not report sentEVAL results and thus it might be possible that DIFFCSE is more robust. Overall the approach of including a difference aware pretraining objective is interesting and could generalize to other applications. It’s interesting that transferring lessons from self-supervised learning in the computer vision literature to NLP requires very careful treatments of the types of transformations applied. It’s almost disappointing that so far the SIMCSE dropout augmentation seems to work the best.
Reference
@inproceedings{Chuang2022DiffCSEDC,
title={DiffCSE: Difference-based Contrastive Learning for Sentence Embeddings},
author={Yung-Sung Chuang and Rumen Dangovski and Hongyin Luo and Yang Zhang and Shiyu Chang and Marin Soljavci'c and Shang-Wen Li and Wen-tau Yih and Yoon Kim and James R. Glass},
year={2022}
}
