Compressing Sentence Representation for Semantic Retrieval via Homomorphic Projective Distillation
Introduction
-
What is the name of the HPD paper?
Compressing Sentence Representation for Semantic Retrieval via Homomorphic Projective Distillation
Xuandong Zhao, Zhiguo Yu, Ming Wu, Lei Li
- What are the main contributions of the HPD paper?
- competitive performance with large vectors while being 8 times faster
- Gain on STS benchmarks compared to similar sized models
- HPD method distills information from a
pretrained teacher model- note: PCA is precomputed from teacher model
- teacher model is not updated during training
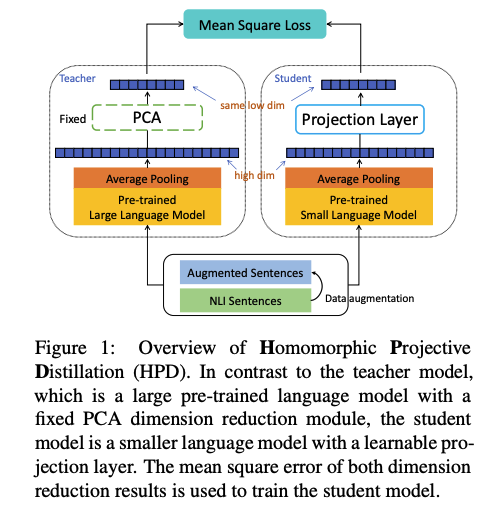
Method
- The HPD method uses the same contrastive objective as
SIMCSE- note: they train on NLI pairs similar to sentence transformers
- in batch hard negatives
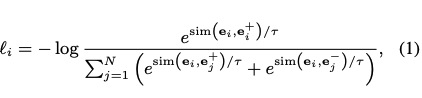
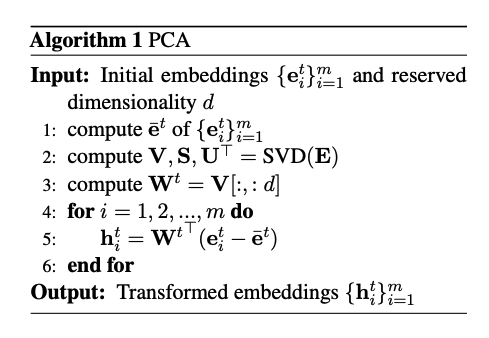
- HPD method compresses the teacher embedding vectors using
PCA- PCA on average pooled embeddings from m sentences
- In HPD the student model is guided using
MSEwith teacher embeddings- teacher embeddings are downsampled using PCA
-
In HPD the PCA dimensions are determined using a
randomly sampled subset of 100k sentences - HPD applied data augmentation using
wordnet substitution and back translation- expand NLI training set to 3 million pairs
- HPD explores
projection and whiteningas dimension reduction baselines- projection is one additional linear layer than downsamples to a lower dimension
- whitening rotates into eigenbases
Results
-
HPD results: competitive performance with vector size of
only 128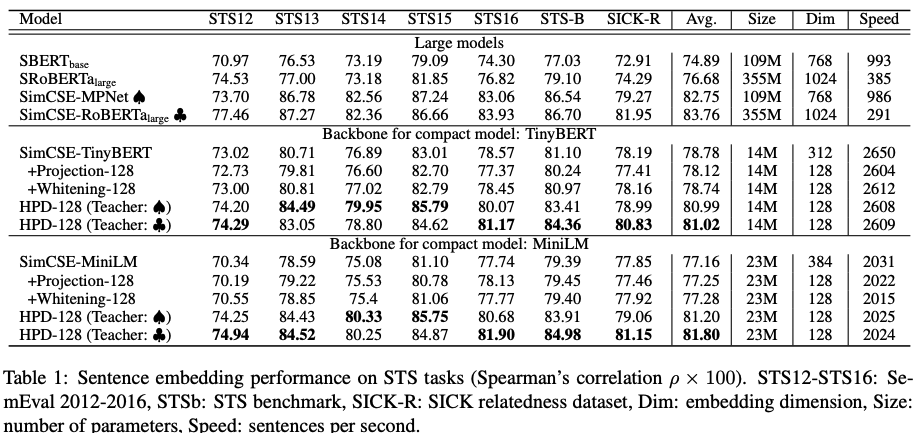
-
HPD shows decent gains in performance from their
simple augmentation method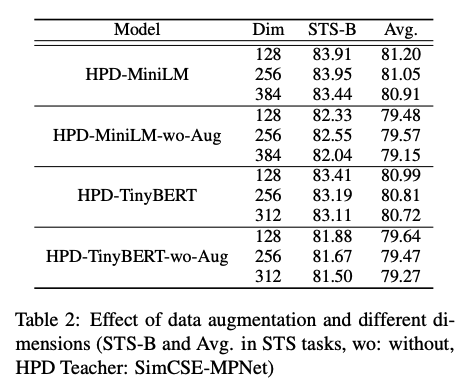
Conclusions
This paper primarily presents a simple distillation method for sentence embedding models. The primary idea is to distill a sentence embedding model by training a student model against the PCA-reduced embeddings from a student model. It’s important to note that only the teacher model is trained first, then the student model. Therefore this approach could be used post hoc to distill any larger sentence embedding model. An interesting ablation that could be performed would be to distill the student model against a teacher with either the projection or whitening dimension reduction methods. This experiment would better convince me of the merits of using PCA for the downsampling in the teacher model. I would be interested in distilling the latest sentence embedding models like promptBERT and DCPCSE. And as the authors state it would be interesting to explore the isotropy of the distilled vectors
Reference
@misc{https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2203.07687,
doi = {10.48550/ARXIV.2203.07687},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.07687},
author = {Zhao, Xuandong and Yu, Zhiguo and Wu, Ming and Li, Lei},
keywords = {Computation and Language (cs.CL), Information Retrieval (cs.IR), FOS: Computer and information sciences, FOS: Computer and information sciences},
title = {Compressing Sentence Representation for Semantic Retrieval via Homomorphic Projective Distillation},
publisher = {arXiv},
year = {2022},
copyright = {Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International}
}
