CHAPTERBREAK: A Challenge Dataset for Long Range Language Models
Type: Paper
Introduction
-
What is the name of the CHAPTERBREAK paper?
CHAPTERBREAK: A Challenge Dataset for Long-Range Language Models
Umass Amherst
- What are the main contributions of the CHAPTERBREAK paper?
- Challenge dataset for Long Range Language Model
- Evaluate BigBird, Routing Transformer
- (Sun et al., 2021; Press et al., 2021) show
that modern LRLMs rely mostly on local context
(i.e., the immediately preceding 1-2K tokens- insensitive to various perturbations applied to more distant context
- perplexity based evaluation
- The CHAPTERBREAK challenge task is to
detect start of next chapter from set of hard negatives- use 8K tokens + identify first 128 tokens of the next chapter
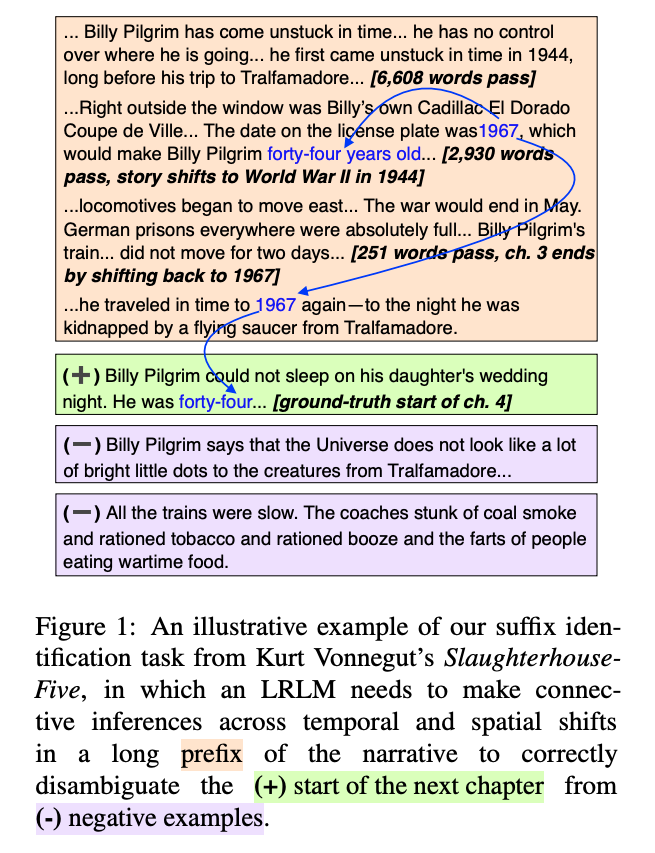
Method
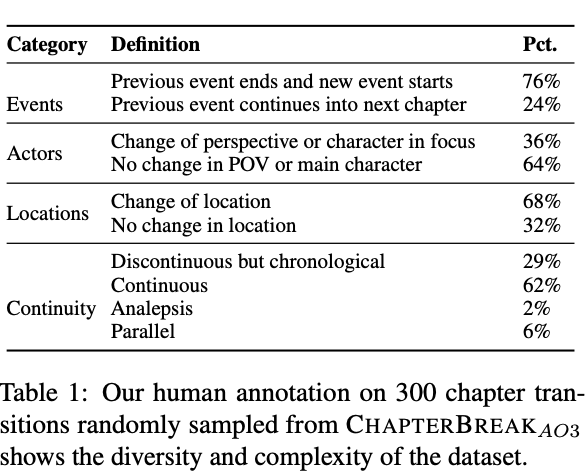
- Types of chapter transitions found in chapterbreak: analepsis is a
flashback to previous point in narrative- from PG19 and fanfiction
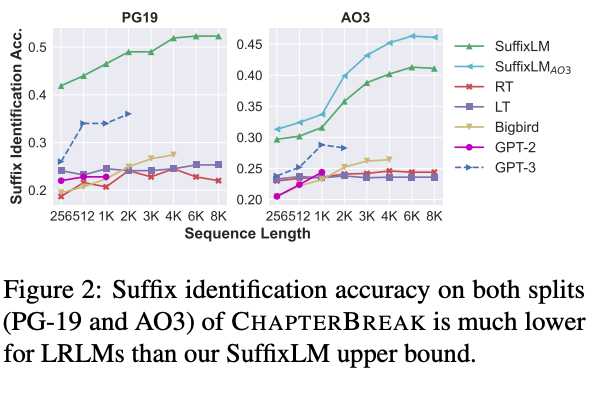
Results
- ChapterBREAK suffix identification is evaluated by which
segment is assigned the maximum probability - ChaperterBreak suffix identification accuracy upper bound in
SuffixLM- accuracy increases with longer prefixes
- perplexity does not necessarily correlate with accuracy
Conclusions
This paper uses a simple method to probe the ability of long range language models. It mostly seems to confirm previous results that models have difficulty reasoning over long spans of text. It would be interesting to see what other tasks could be developed exploiting structure from books.
Reference
@inproceedings{sun-etal-2022-chapterbreak,
title = "{C}hapter{B}reak: A Challenge Dataset for Long-Range Language Models",
author = "Sun, Simeng and
Thai, Katherine and
Iyyer, Mohit",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies",
month = jul,
year = "2022",
address = "Seattle, United States",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2022.naacl-main.271",
pages = "3704--3714",
abstract = "While numerous architectures for long-range language models (LRLMs) have recently been proposed, a meaningful evaluation of their discourse-level language understanding capabilities has not yet followed. To this end, we introduce ChapterBreak, a challenge dataset that provides an LRLM with a long segment from a narrative that ends at a chapter boundary and asks it to distinguish the beginning of the ground-truth next chapter from a set of negative segments sampled from the same narrative. A fine-grained human annotation reveals that our dataset contains many complex types of chapter transitions (e.g., parallel narratives, cliffhanger endings) that require processing global context to comprehend. Experiments on ChapterBreak show that existing LRLMs fail to effectively leverage long-range context, substantially underperforming a segment-level model trained directly for this task. We publicly release our ChapterBreak dataset to spur more principled future research into LRLMs.",
}
